2014 - Aeroboat
Propelled by the same Rolls-Royce Merlin V12 engine that powered Britain's Spitfires to victory in World War II: the yacht designers, Claydon Reeves, also based the boat’s design on the ‘sleek lines’ of the famous fighter planes. It can ‘fly’ like a jet across water at 109mph. The boat costs £3 million.
2012-2013 - Synthetic meat
The meat is grown from stem cells, marking the first step for a possible revolution in meat production. However, taste tests (2013) and costs currently limit the project.
2012-2013 - Electric vehicle stations
As of December 2012, there were around 50,000 non-residential slow charging points and about 2,000 fast chargers deployed in the U.S., Europe, Japan and China. As of March 2013, the United States had 5,678 public charging stations across the country with 16,256 public charging points. As of November 2012, about 15,000 charging stations had been installed in Europe
The world's top-selling highway-capable all-electric cars are the Nissan Leaf, with global sales of over 71,000 units by mid July 2013.
2012 - Sound barrier broken by body
Skydiver Felix Baumgartner breaks the sound barrier without the use of a vehicle, diving 24.23 miles and reaching a speed of 843.598 mph.
-
The design for the McLaren MP4-12C supercar marks the first car fully designed and built by the company in over a decade. Car launched 2011.
2008 - Carbon capture and storage
First pilot plant.
2007 - Stem cells
James Thomson and Shinya Yamanaka convert human skin into stem cells, previously the cells had to be harvested from human embryos.
2007 - Solar Atlantic Crossing
Sun21 completes the first solar-powered crossing of the Atlantic Ocean taking 29 days.
2007 - Skysails
SkySails is piloted on cargo ships. A 160 metre square kite, controlled by computers, its makers believe it could cut the fuel costs of cargo ships by 10 to 35 per cent.
2006 - Water 'creation'
Aqua Sciences develop technology to extract water from the atmosphere. The device works virtually anywhere that is inhabited by human beings, delivering clean water for drinking, industry etc.
2006 - Turbosteamer
BMW develops prototype turbosteamer technology. It converts 80 per cent of exhaust heat into power.
2006 - Institution of Mechanical Engineers first female CE
IMechE appoint Ruth Spellman Chief Executive.
2006 - Cosmoplane test flight
Russia’s Institute of Applied Mechanics developed a new aircraft: it takes off and lands like an ordinary plane, but it behaves like a spacecraft for the rest of the flight. The aerospace craft is expected to fly at heights between 100-200 kilometres and with speed as high as 30 thousand kilometres per hour. It takes the vehicle 20 minutes to fly from Moscow to Paris and 50 minutes to New York. The cosmoplane uses hypersonic engines fuelled by oxygen and hydrogen. Tests of plane’s 1:25 scale model by institute’s experts proved to be successful.
2004-2010 - Graphene
Graphene is one of the crystalline forms of carbon: carbon atoms are arranged in a regular hexagonal pattern. Graphene can be described as a one-atom thick layer of the layered mineral graphite. High quality graphene is very strong, light, nearly transparent and an excellent conductor of heat and electricity. The method for isolating the layers is developed by Andre Geim and Konstantin Novoselov.
In 2010 a Nobel Prize in Physics was granted to Geim and Novoselov "for groundbreaking experiments regarding the two-dimensional material graphene".
2004 - Injection by soundwave
SonoPrep is invented by bioengineer Robert Langer. The device delivers medication by sound waves rather than injection.
2003 - Hybrid electric vehicle
The Renault Kangoo is produced. It is the first plug-in hybrid electric vehicle, which can be recharged from the mains, and does not require conventional fuel for short trips.
2003 - Clear Skies
The Clear Skies renewable energy grant scheme is launched in the UK.
2002 - Scramjet
The HyShot supersonic ramjet (scramjet) makes its first successful flight at Mach 7.6, over seven times the speed of sound. It is a jet engine powered by oxygen which is taken from the atmosphere as it flies, compressed and mixed with a small amount of hydrogen to produce an explosion.
2002 - Hydrogen fuel car
General Motors reveal the Hy-Wire, a revolutionary concept car powered by hydrogen fuel cells. It is controlled electronically, removing the need for steering wheels, pedals and other traditional features of the automobile.
2002 - Falkirk Wheel opens
The Falkirk Wheel is a rotating boat lift in Scotland. It connects the Forth and Clyde Canal with the Union Canal.
2001 - Segway PT
The two wheeled, self-balancing, electric vehicle is unveiled by inventor Dean Kamen.
2000 - Blyth wind farm
Blyth offshore wind farm, the first in the UK, opens off the Northumberland coast. Its 2MW turbines are the largest offshore turbines in the world.
1999 - Millennium Wheel
The Millennium Wheel is hoisted into position, transforming the London skyline.
1998 - Robot assisted heart bypass
The first robot assisted heart bypass operation is performed by Dr. Ralph Damiano at Pennsylvania State Hospital, USA.
1998 - International Space Station
Work begins on the ISS, a collaboration between the USA, Canada, Russia, Europe and Japan.
1998 - Formula Student
Formula Student is launched, one of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers most popular events. Teams of students design and build a single-seater racing car, which then faces three days of endurance tests and scrutiny by professional engineers and industry experts.
1997 - Thrust SSC
Thrust SSC sets the land speed record, reaching 763.044 mph. It is the first car to officially break the sound barrier, it is jet-propelled. Designed by Richard Noble and driven by Andy Green.
1997 - The Institution of Mechanical Engineers first female President
The IMechE's 150th anniversary is marked by the appointment of its first female President, Pam Liversidge.
1997 - Kyoto Protocol
55 nations agree to binding obligations to reduce emissions of greenhouse gases, aviation and shipping are excluded. The USA refuses to sign.
1997 - Hybrid automobile
The Toyota Prius is the first mass-produced hybrid automobile. It goes on sale in Japan in 1997, and is introduced worldwide in 2001.
1997 - Deep Blue
IBM's super computer beats Russian world chess grandmaster, Garry Kasparov. Marking the first defeat of a human by a machine in chess.
1996 - Solar crossing of Pacific
Kenichi Horie completes the first solar powered crossing of the Pacific Ocean.
1995 - Space walking Briton
Dr Michael Foale performs the first space walk by a British-born American citizen.
1995 - M-theory
A new universal theory of everything is proposed by Edward Witten, uniting attempts to reconcile gravity with quantum physics (string theories). Witten's theory is championed by Stephen Hawkin, but remains incomplete.
1995 - GPS
Conceived by Roger Easton, GPS (Global Positioning System) measures time and location in all weathers using a network of satellites.
1995 - Fermat's Last Theorem
358 years after it is conceived, Pierre de Fermat theorem (or conjecture) is proved by Andrew Wiles. Famously Fermat placed it in the margin of a copy of Arithmetica but he claimed he had a proof that was too large to fit in the margin. It states that, no three positive integers a, b, and c can satisfy the equation an + bn = cn for any integer value of n greater than two.
1994 - GM crops
Genetically modified crops, supposedly more resistant to disease and faster growing, are introduced.
1993 - Fuel cell bus
The first bus powered by a fuel cell is completed.
1993 - Dyson vacuums founded
Bagless vacuum cleaners are produced by James Dyson's new company. In 2005 they become the market leader in the USA.
1991 - UK wind farm
Delabole wind farm opens, the first in the UK.
1991 - First Briton in space
Helen Sharman is the first Briton is space, on-board the Soviet space capsule, Soyuz TM-12.
1990-1994 - Channel Tunnel
Construction workers drilling the Channel Tunnel meet in the middle, physically joining the UK to Europe for the first time in the modern age. The Channel Tunnel is formally opened by the Queen and the French President Francois Mitterrand in 1994.
1989-1990 - World Wide Web
Tim Berners-Lee invents the web, a system of interlinked hypertext documents accessed via a web browser.
1987 - World Solar Challenge
The World Solar Challenge is founded. It is a biannual solar-powered car race, run over 1877 miles from Darwin to Adelaide. The first winner reaches a speed of 42mph.
1984 - Thames Barrier opens
The 520 metre barrier completes construction, aiming to prevent flooding from rising tides and storm surges.
1984 - Macintosh launched
Apple Computer launch the first commercially successful computer to use a mouse and graphical user interface.
1983 - Sonic toothbrush
Philips invent the sonic toothbrush.
1983 - Maglev
The world's first maglev (magnetically levitating) train begins operating in the UK as a shuttle between Birmingham airport and Birmingham International Railway Station, it is replaced a few years later.
1982 - Volkswagen photovoltaic arrays
Volkswagen began testing photovoltaic arrays mounted on the roofs of vehicles.
1981-1988 - Stealth aircraft
The US F-117A Nighthawk is the first aircraft to use stealth capability. It is produced by Lockheed Aeronautical Systems Co. The maiden flight for the type was conducted in 1981, and it achieved initial operating capability status in October 1983. The F-117 was "acknowledged" and revealed to the world in November 1988.
1981-1984 - 3D printing (additive manufacturing)
In 1981, the first published account of a printed solid model was made by Hideo Kodama of Nagoya Municipal Industrial Research Institute. However, the man most often credited with inventing the 3D printer is Charles W. Hull, who first patented the term 'stereolithography' (defined as "system for generating three-dimensional objects by creating a cross-sectional pattern of the object to be formed") in 1984.
1981 - Space shuttle
Space Shuttle Columbia is launched, the first space shuttle flight. It is also the first time that solid rocket fuels are used in a US manned launch.
1981 - Solar One
Solar One is completed. The 126 acre pilot solar-thermal project produces 10MW using 1818 mirrors or heliostats. The heliostats concentrate the suns rays on a collector tower, which transfers the energy to a substance which stores the heat for later use.
1980 - Rubik cube
The Hungarian architect Erno Rubik's cube goes on sale, the 3D twisting cube becomes the best selling toy of all time.
1978 - Village photovoltaic system
The world's first village photovoltaic system is installed at Papago Indian Reservation, Schuchuli, Arizona.
1978 - Regenerative braking
David Arthurs develops the regenerative braking system.
1976 - Concorde
The first Concorde jets carrying commercial passengers take off simultaneously from London to Bahrain and Paris to Rio de Janeiro.
1975 - North Sea pipeline
The North Sea pipeline is opened, bringing ashore 40,000 barrels of oil a day to the Grangemouth Refinery on the Firth of Forth, Scotland.
1974 - Edinburgh Duck
Professor Stephen Salter develops the Edinburgh Duck, a device which can stop 90% of wave motion; of that, 90% can be converted into electricity.
1974 - Catalytic converter
General Motors introduce the catalytic converter, a device to reduce the toxicity of emissions from an internal combustion engine.
1973 - Mobile phone
Dr Martin Cooper invents the mobile phone.
1973 - Airbag
The first car to be sold to the general public with an airbag as a standard feature is the Oldsmobile Tornado. It is available only on the passenger side.
1972-1977 - MRI scanner
Dr Raymond Damadian patents the world's first MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging scanner), he undertakes the first full-body scan in 1977.
1971 - Holography
Dennis Gabor pioneers holography, a technique of recording and playing back images that can be viewed from a range of angles as if they existed in 3D space.
1970 - Boeing 747
A Boeing 747 jet arrives at Heathrow Airport in London after completing its maiden flight from New York.
1970 - Apollo 13
Apollo 13, carrying three US astronauts, splashes down safely after a five day rescue operation in space. The trouble is caused by an explosion on board the spacecraft during their journey to land on the Moon.
1969-1976 - Supersonic commercial flight
Aérospatiale-BAC Concorde, a turbojet-powered supersonic passenger airliner or supersonic transport (SST) is first flown in 1969, Concorde entered service in 1976 and continued commercial flights for 27 years.
It is one of only two SSTs to have entered commercial service; the other was the Tupolev Tu-144. Concorde was jointly developed and produced by Aérospatiale and the British Aircraft Corporation (BAC) under an Anglo-French treaty.
1969 - Institution of Locomotive Engineers
Institution of Mechanical Engineers merge with the Institution of Locomotive Engineers, creating the Railway Division.
1968 - Jet ski
Clayton Jacobsen patents the jet ski. Kawasaki buy the rights.
1967-1969 - ATM/Cash point
The world's first Automatic Teller Machine (ATM) is installed at the Rockville Centre, Long Island at a branch of Chemical Bank, 1969. It was invented by Don Wetzel.
Barclays Bank had introduced a simpler version two years previously at a branch in North London, but it used paper vouchers (rather than the magnetic strip technology used by the Chemical Bank's ATM).
1966 - First lunar landing
The first scheduled unmanned soft landing on the moon surface is made by the Soviet Luna 9.
1964 - Tokaido Shinkansen
The Tokaido Shinkansen opens. It is the first high speed train in the world, travelling between Tokyo and Shimonoseki at speeds of 130 mph.
1964 - Mouse
Dr Douglas Engelbart invents the computer mouse.
1964 - Land speed record
British speed pioneer Sir Donald Campbell sets a new land speed record of 429mph in his car, Bluebird. Campbell held and broke a number of land and water speed records throughout his career.
1961 - UK carwash
The first fully automated car wash in the UK opens by Stirling Moss on Brompton Road, London.
1960 - Internal pacemaker
The internal heart pacemaker is patented by Wilson Greatbatch. See 1950 - External pacemaker.
1960 - Bubblewrap
The Sealed Air Corporation is formed by US engineers, Alfred Fielding and Marc Chavannes, in order to market their new invention, bubble wrap.
1959 - Hydrogen fuel cell
Francis Thomas Bacon builds the first modern fuel cell, fed with high pressure hydrogen.
1958 - Photovoltaic satellite
The first photovoltaic powered satellite is launched in the US.
1957 - Monorail
Ueno Zoo, Tokyo, is the site of the first monorail.
1956-2001 - Artificial heart
The artificial heart was patented in 1956 by Dr. Paul Winchell.
In 1982 the first 'successful' artificial heart (the Jarvik-7) is designed by Robert Jarvik, it is received by Barney Clark: William DeVries performs the surgery. He lives for 112 days, although the heart was intended to last a lifetime it is the first occurrence of a patient living beyond surgery. Jarvik continued to improve the device for example, working on the Jarvik 2000, a thumb-sized heart pump.
Various incarnations of the technology sought to replace transplant but it was not until 2001 that a major breakthrough occurred.
In 2001 the AbioCor artificial heart is invented by AbioMed. It is fully implantable within a patient, due to a combination of advances in miniaturization, biosensors, plastics and energy transfer. The AbioCor runs on a rechargeable source of power. The internal battery is charged by a transcutaneous energy transmission (TET) system, meaning that no wires or tubes penetrate the skin and therefore there is less risk of infection
1956-1959 - Hovercraft
The modern hovercraft is invented by Christopher Cockerell. He produced his first hovercraft, SRN 1, in 1959.
1956 - First commercial nuclear power station
Calder Hall, the world's first large-scale commercial nuclear power station, is connected to the national grid.
1955 - Diesel electric trains
Diesel electric trains are first introduced in the UK.
1954 - Nuclear power station
The world's first nuclear power station opens at Obninsk, near Moscow. Britiain's first station opens in the same year, at Harwell.
1953-1969 - Colour television
The first successful colour television system is designed by the Radio Corporation of America. Broadcasting begins on 17 December 1953. It was introduced in the UK on BBC Two for Wimbledon coverage on July 1, 1967. The launch of the BBC2 "full" colour service took place on December 2, 1967. Some British TV programs, however, had been produced in colour even before the introduction of colour television in 1967, for the purpose of sales to American, Canadian, and Filipino networks. BBC One and ITV started colour transmissions November 15, 1969.
1953 - Heart-lung machine
The heart-lung machine is developed by John Gibbon of Philadelphia.
1953 - Airbag
The first patent for the airbag is taken out by American naval engineer, John Hetrick. It is perfected by American inventor, Allen K Breed, in 1968.
1952 - Mechanical heart valve
The first human implant of a mechanical heart valve is made.
1951 - Electricity from nuclear fission
The first usable electricity from nuclear fission is produced at the National Reactor Station, Idaho. Four years later, the neighbouring town of Arco is the first to be powered by nuclear energy.
1950 - Microwave
Percy Lebaron Spencer, from Massachusetts, patents the first microwave oven.
1950 - External pacemaker
Dr Mark Lidewell invents the pacemaker: a medical device that uses electrical impulses, delivered by electrodes contracting the heart muscles, to regulate the beating of the heart. See 1960 - Internal pacemaker.
1950 - Cardiac pacemaker
Canadian John Hopps invents the cardiac pacemaker, although the first model is too large to fit into the human body.
1949 - De Havilland Comet
The de Havilland Comet, the world's first jet airliner, makes its maiden flight.
1947 - Institution of Automobile Engineers
Institution of Mechanical Engineers merges with the Institution of Automobile Engineers, creating the Automobile Division.
1947 - Breaking the sound barrier
Chuck Yeager is the first person to break the sound barrier in level flight, flying the X-1.
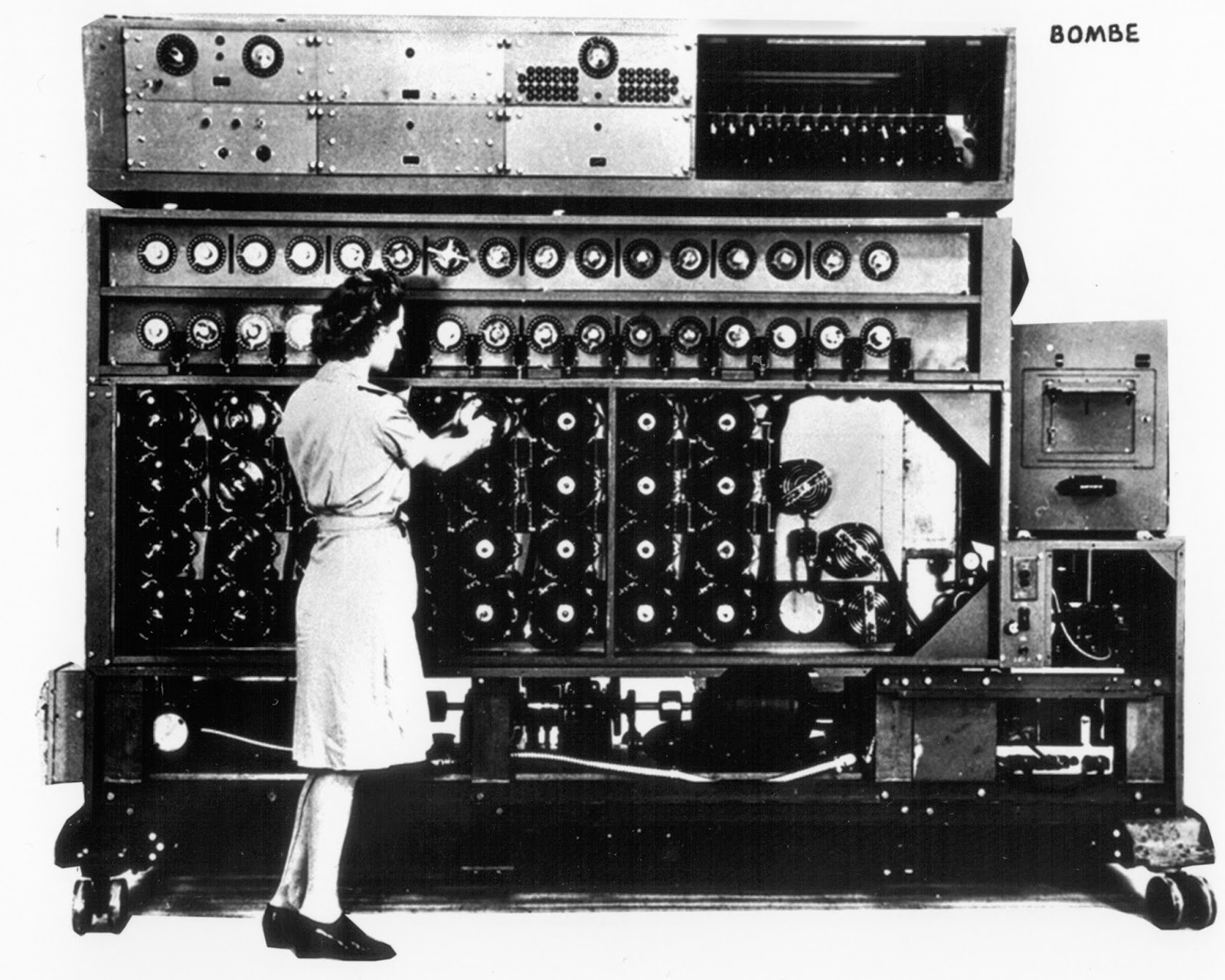
1945 - Turing-Welchman Bombe
Alan Turing develops the Turing-Welchman Bombe, an electromechanical machine capable of deciphering the German enigma codes, at Bletchley Park.
1945 - James Clayton lecture
First James Clayton lecture (Institution of Mechanical Engineers premier award of its typ) is authorised by Council. Frank Whittle presents ‘The early history of the Whittle gas turbine’ to a packed house. Read the papers.
1944 - Calculator
American Howard Aiken develops the first fully automatic, large scale calculator, known as the Harvard Mark I. It has over 750,000 parts.
1944 - PLUTO
The Pipeline Under the Ocean (PLUTO) was designed to supply petrol from storage tanks in southern England to the advancing Allied armies in France in the months following D-Day. It was fully operational by June 14 1944.
1943 - Dialysis machine
The artificial kidney (dialysis machine) is tested for the first time.
1942 - Nuclear chain reaction
Enrico Fermi demonstrates the first self supporting nuclear chain reaction in a laboratory at the University of Chicago.
1941 - Gloster E28/39
The Gloster E28/39 is the first aircraft to fly using Whittle's jet engine.1939 - First working helicopter
The first working helicopter is constructed by Sikorsky.1939 - First rocket powered flight
Flight Captain Erich Warsitz pilots the first rocket powered aircraft, the He176.1939 - First jet powered flight
The first jet aircraft to fly is the Heinkel He 178, powered by an He S3B engine designed by Hans von Ohain. The plane is piloted by Flight Captain Erich Warsitz, who also piloted the first jet powered aircraft.1938 - Tumble dryer
Hamilton's Manufacturing Company produces the first commercial tumble dryer, invented by J Ross Moore.

1938 - Steam locomotive speed record broken
The Mallard locomotive gains the world speed record for steam locomotives at 126 mph (203 kph). It was designed by the renowned locomotive engineer Sir Nigel Gresley.1937-1959 - Photocopier
Chester F Carlson invents the photocopier. It is not patented until 1942, and it is not until 1959 that the first commercial machine goes on sale by the Haloid Company, later renamed the Xerox Corporation.1937 - Jet engine
1936-1938 - Spitfire
The Spitfire fighter plane, designed by Reginald Mitchell, has its maiden flight. It enters RAF service in 1938.1935; 1952 - Biro
Laszlo Biro produces the ballpoint pen commercially. It is not until 1952 that the most popular ballpoint pen in the UK, the Bic, is first produced by French manufacturer Marcel Bich.1932-1939 - BBC broadcasting, television and radio
The BBC makes the first televised broadcast, from Alexandra Palace, London on 22nd August. From December radio broadcasting widens: on the 19th The Empire Service (precursor of the World Service) launches; and on the 25th King George V becomes the first monarch to deliver a Christmas Day message by radio, on the Empire Service.
Four years later, the BBC opens the world's first regular high-definition television service:
- 1937
- 12 May – First use of TV outside broadcast van, for the coronation procession of King George VI.
- 21 June – The BBC broadcasts television coverage of the Wimbledon Tennis Championships for the first time.
- 16 September – The BBC makes the world's first live television broadcast of a football match, a specially arranged local mirror match derby fixture between Arsenal and Arsenal reserves.
- 1938
- 3 January – The BBC begins broadcasting its first foreign-language radio service, in Arabic.
- 30 April – The BBC broadcasts television coverage of the FA Cup for the first time.
- 27 September – Start of the European Service on radio, broadcasting in French, German and Italian. Portuguese and Spanish are added before the start of the Second World War.
- 1939
- 1 September – The BBC Television Service is suspended, about 20 minutes after the conclusion of a Mickey Mouse cartoon (Mickey's Gala Premiere), due to the imminent outbreak of the Second World War, amid fears that the VHF transmissions would act as perfect guidance beams for enemy bombers attempting to locate central London – also, the technicians and engineers of the service will be needed for war efforts such as the RADAR programme. On radio, the Home Service replaces the National and Regional Programmes.
- 1937
1932 - Piccadilly Circus electrified
In London, Piccadilly Circus lights are lit by electricity for the first time.1931 - Wind generator
1930 - Quick freeze machine
Clarence Birdseye patents the 'Quick Freeze Machine', reducing the time needed to freeze food from three days to a few minutes.1929 - Transatlantic non-stop flight
English air pioneers John Alcock and Arthur Brown complete the first non-stop transatlantic flight from Newfoundland to Ireland.1929 - Jet engine
1927 - Transatlantic airplane flight
1926 - Rocket propellant
The world's first liquid rocket propellant is launched by Robert Goddard, near Worcester, Massachusetts.1924-1926 - Television
Television is demonstrated for the first time by John Logie Baird at Selfridges, London, 1926. It used a mechanical system of rotating discs which had been patented in 1924.1924 - Wembley Stadium
On 23 April 1924 Wembley Stadium is officially opened by King George V.1924 - IMechE first female member
Verena Holmes becomes the first woman to be elected as an Institution of Mechanical Engineers member.1924 - First rotary engine
Felix Wankel develops the Wankel engine, the world's first rotary engine.1921 - First IMechE Local Branch
The first Institution of Mechanical Engineers local members’ branch is created in Birmingham, the birthplace of the Institution (1847) before its move to London in 1877.1919 - Transatlantic airship crossing
1919 - Pop up toaster
Charles Strite designs the pop-up toaster. It is patented in 1921 and launched in 1926.1917 - First aircraft carrier
HMS Argus is launched, the first vessel to be designed for use as an aircraft carrier.1915-1917 - Dual power/hybrid car
'Dual Power’ developed by Woods Motor Vehicles. It has a four cylinder internal combustion engine and an electric motor. For speeds under 15mph the car is powered by the electric motor, while the internal combustion engine takes it up to a maximum speed of 35mph. Around 600 are made up to 1918. The first was produced in 1917.1914 - Tank
1914 - First car wash
The world's first car wash, the Automated Laundry, opens in Detroit, Michigan.1914 - First bomber aircraft
The German airship Zeppelin (named after its pioneer, Count Ferdinand Graf von Zeppelin) is the world's first bomber aircraft.1913- Assembly line
The assembly line is introduced to manufacture Ford Model Ts. As a result, Ford's cars came off the line in three-minute intervals, much faster than previous methods, reducing production time by a factor of eight (requiring 12.5 hours before, 93 minutes afterwards), while using less manpower.1913 - IMechE Graduateship
The Institution of Mechanical Engineers commences its own graduateship examinations in a drive to improve and control the training. The tests are not entirely technical; general knowledge papers tested candidates reading of Chaucer and Tennyson.1911 - Refrigerator
General Electric launch their first home-market refrigerator.1911 - Electric starter motor
The electric starter motor for automobiles is invented by Charles Kettering.1908 - Electric washing machine
1908 - Electric vacuum cleaner
James Murray Spangler develops the first electric powered vacuum cleaner. The patent is bought by Hoover.1907 - Helicopter flight
French brothers Jacques and Louis Breguet's helicopter makes the world's first flight.1907 - Brooklands
Brooklands, the first purpose built, off-road race track, is built at Weybridge in Surrey.1906 - Grand prix
The French Grand Prix, the first of its kind, takes place on a 100km road circuit near the town of Le Mans. The total distance run is 1100km.1904 - Geothermal electricity
A geothermal electric generator is built at Larderello, Italy.1901 - First hybrid car
Ferdinand Porsche designs the ‘Mixte’, the first recorded petroleum electric hybrid vehicle on record. It uses a petrol motor to power a generator, which in turn powers a hub motor, with a battery pack for backup. It has a top speed of 35mph.1900-1901 - Escalator
Charles D Seeberger joins forces with the Otis Elevator Company to produce the first practical device with moving stairs. It is exhibited at the Paris Exposition of 1900. The first commercial version is installed at Gimbel's department store, Philadelphia, the following year.1900 - The Zeppelin
Ferdinand von Zeppelin develops the world’s first successful dirigible – the Zeppelin.1900 - Peanut oil engine
Diesel demonstrates an engine which runs on peanut oil.1899 - IMechE Headquarters
Institution of Mechanical Engineers constructs Storey’s Gate headquarters, later known as 1 Birdcage Walk. A Graduates’ section for younger members is created and immediately makes its mark when the first ever paper on automobiles is delivered.1896 - Michelin & Cie
Pneumatic tyres are first used on motor cars by Michelin & Cie, France.1896 - First flight
Samuel Pierpont Langley makes the first sustained flight by a heavier-than-air powered, unmanned aircraft: the Number 5 model, driven by a miniature steam engine, flew half a mile in 90 seconds over the Potomac River near Washington, D.C. In November that year the Number 6 flew more than five thousand feet.1896 - British petrol-driven car
Frederick Lanchester develops the first full sized British petrol-driven car.1895 - X-rays
Wilhelm Roentgen discovers X-rays. In recognition of his work, he is awarded the first Nobel Prize for Physics in 1901. He refuses to patent his work, considering it a gift to humankind.1895 - First petrol driven bus
The world's first petrol driven bus is created in Germany by the Netphener Omnibusgesellschaft, who convert a Benz truck. It is capable of carrying eight passengers.
1895 - First Lanchester automobile
Frederick Lanchester and his brother construct a production model, one of the earliest petrol automobiles in England.1893 - Lawnmower
James Sumner of Leyland, Lancashire, develops the first motor driven lawnmower. It is powered by steam and weighs two tonnes.1893 - Hydroelectric dam
The first dam designed specifically for generating hydroelectricity is built across the Colorado River.1893 - Ferris wheel
George Washington Ferris builds the first Ferris wheel for the World Fair at Chicago.
1892-1898 - Diesel engine
Rudolf Diesel invents the engine in 1892. It is patented six years later.1891 - Electric toaster
Crompton and Company invent the electric toaster. The same company later launches the electric kettle, exhibited 1892.1888 (1935) - Ballpoint pen
American John Loud invents the ballpoint pen but it is not produced commercially until 1935.1888 - Pneumatic tyre
John Dunlop invents the pneumatic tyre.1888 - Electricity generation
A brush post mill is used to generate electricity in Cleveland, Ohio; in 1891 La Cour windmill is used to generate electricity.1887 - Radar
German physicist Heinrich Hertz develops radar.
1886 - Four-wheeled motor vehicle
The first four-wheeled motor vehicle is produced by Daimler, working with Wilhelm Maybach.1886 - Commercial dishwasher
Josephine Cochrane invents and patents the first commercial dishwashing machine. Apparently she was dissatisfied with the treatment her servants were subjecting her china to and disliked doing the washing up herself.
1885 - Motorbike
Gottlieb Daimler builds the world's first motorbike.1885 - Automobile
Karl Benz creates the first purpose built automobile.
1884 - Parson's Steam turbine
Sir Charles Parsons invents the modern steam turbine, whose first model was connected to a dynamo that generated 7.5 kW of electricity. The invention made cheap and plentiful electricity possible and revolutionised marine transport and naval warfare, amongst other industries.
1884 - Machine gun
Hiram Maxim demonstrates the first prototype Maxim gun, the first truly automatic machine gun.1882 - First trolley bus
Siemens install the world's first trolley bus service along the Kurfürstendamm in Berlin.1881 - Metal detector
Alexander Graham Bell invents the metal detector, with limited initial success. When President James Garfield is shot doctors asks Bell to locate the bullet but he couldn't. However, there is some debate as to whether this was due to metal in the bed.1879 - Long distance pipeline
The first long distance pipeline is built in the United States by Tide Water Oil Company, running from Pennsylvania to the East Coast.1879 - Cash register
Barman James Ritty invents the cash register.1878-1881 - First two-stroke petrol engine
Sir Dugald Clerk develops the first two-stroke petrol engine (or two-cycle engine), 1878. It is patented three years later. The crankcase-scavenged engine, employing the area below the piston as a charging pump, is generally credited to Englishman Joseph Day.1878 - Solar powered steam engine
A solar powered steam engine is exhibited in Paris.1877 - Tynewydd Colliery
1877 - IMechE moves to London
The Institution of Mechanical Engineers moves to London, with a rented headquarters at 10 Victoria Chambers, Victoria Street.1876 - Telephone
1868 - Westinghouse compressed air brake
George Westinghouse invents the compressed air locomotive brake.1868 - Typewriter
Christopher Latham Sholes patents the first commercial typewriter.1868 - Traffic signals
John Peake Knight invents the first traffic signals. They are installed at the junction of George Street and Bridge Street in Westminster, London. His invention was instigated by the 1102 people who were killed and 1334 injured on roads in London, in 1866.1865 - First pipeline
The world's first pipeline is built, out of wood. Nine miles long, it carries crude oil from the well at Pithole, Pennsylvania.1863 - First underground railway
The world's first underground railway, the Metropolitan Line, is opened in London, running from Bishop's Road, Paddington to Farringdon.1862 - Man-made plastic
Alexander Parkes invents the first man-made plastic by mixing pyroxylin with alcohol and camphor. He called the resulting hard, transparent and flexible material Parkesine.1861 - Solar power
Auguste Mouchot is granted a patent for running a motor by solar power.1860 - Singer sewing machine
Isaac Singer builds the first commercially successful sewing machine. The company he founds becomes the world's largest manufacturer of sewing machines.1858 - Transatlantic cable
The first transatlantic cable is laid by American Cyrus Field.
1858 - The Great Eastern
Isambard Kingdom Brunel's five funnelled steamship The Great Eastern is launched.1857 - Elevator
The first mechanical elevator is installed at E V Haughwout and Company department store, Broadway, New York City.1857 - Blast furnace
William Kelly invents the blast furnace for steel production.
1856 - Bessemer steel process
Bessemer's process for steel production is introduced. This is the first process commercially viable process for producing steel, leading to the replacement of iron and other metals with steel.1855 - Rayon
George Audemars invents Rayon but is not able to manufacture it commercially.1854 - Halladay windmill
Daniel Halladay patented the first commercially successful self-governing windmill.1854 - Bunsen burner
Bunsen burners are first produced by German physicist and chemist Robert Bunsen.1852 - Burglar alarm
American manufacturer Edwin Holmes develops the burglar alarm.1851 - Washing machine
James King is awarded the first patent for a mechanical clothes washing device: a hand powered, rotating cylinder machine with a drum.
1851 - The Great Exhibition
The Great Exhibition is held at Crystal Palace, London. It was a showcase for manufacturers and industrialists, and was a great success, attracting over 6 million visitors and making a profit of £187,000 for the nation.1851 - First IMechE London Meeting
In the same year as The Great Exhibition, the Institution of Mechanical Engineers first London meeting is held.1850 - Underwater telegraph cable
The first underwater telegraph cable is laid between France and England.1850 - Dishwasher
The first dishwasher is developed by Joel Houghton.1847 - Institution of Mechanical Engineers founded
The Institution of Mechanical Engineers is created, ‘to give an impulse to inventions likely to be useful to the world’. 56 engineers and manufacturers meet at the Queen’s Hotel, Birmingham for the inaugural meeting. George Stephenson is elected first President. IMechE bases itself in Newhall Street, Birmingham.1843 - Fax Machine
Alexander Bain develops the first fax machine.1841 - Stapler
Samuel Slocum patents the stapler.
1840 - Measuring machine
Joseph Whitworth develops his measurement machine, previously accuracy was up to one sixteenth of an inch was a good workman. Whitworth’s measured up to one two-millionth of an inch: allowed him to produce standard measures and gauges. Uniformity was extended to the still famous Whitworth system of thread screw threads.
1839-1842 - Steam hammer
James Nasmyth invents the steam hammer circa 1839, patenting it in June 1842.1839 - Fuel cell
The first fuel cell, combining hydrogen and oxygen to produce electrical power, is developed by William Robert Grove.1837 - Mechanical refrigeration
The first patent for mechanical refrigeration is issued to American Jacob Perkins.
1830 - Liverpool & Manchester Railway
The Liverpool & Manchester Railway opens. It is the first purpose built passenger railway in the world.1829 - Rainhill Trials
The Rainhill Trials are held to determine whether steam locomotives could be capable of providing the motive power for the Liverpool & Manchester Railway. The contest is won by Rocket, Robert Stephenson’s locomotive based upon the design principles of George Stephenson.1827-1837 - Water Turbine
The first water turbine is developed and produced by Benoît Fourneyron.
1825 - First passenger locomotive
1822 - Difference engine
Mathematician Charles Babbage builds his difference engine (or automatic mechanical calculator) to improve significantly the accuracy of the calculations in the production of arithmetical tables.1813 - First cotton-to-cloth mill
Francis Lowell's investor group builds Waltham Mills, Massachusetts. It is the first to place cotton-to-cloth production under one roof. The group was incorporated as the Boston Manufacturing Company in 1814.1810 - Steam-powered printing press
1808 - 'Catch-me-who-can'
Richard Trevithick builds a circular railway track nicknamed the 'Catch-me-who-can', to demonstrate his steam engine. Entrance to the "steam circus" cost one shilling and included a ride; it was intended to show that rail travel was faster than by horse.1804 - Jacquard Loom
Joseph Marie Jacquard invents the Jacquard Loom. Through the use of punched cards, the loom is capable of weaving complex designs.1804 - Gas lighting
Friedrich Winzer (also known as Winsor) patents gas lighting.
1802-1804 - Pen-y-Darren steam locomotive
Richard Trevithick builds a prototype steam locomotive at Pen-y-Darren, 1802. Selling the patent the next year. In 1804 a revised version successfully carried 10 tons of iron, 5 wagons and 70 men for 9.75 miles in 4 hours and 5 minutes (at an average speed of approximately 2.4 mph). Making it the first steam locomotive to undertake practical work.
1801 - Trevithick steam carriage
Richard Trevithick builds the first steam-carriage designed for road travel.1800 - Battery
Alessandro Volta invents the battery.1794 - Cotton gin
Eli Whitney patents the cotton gin, which automates the process of separation cotton seed from short-staple cotton fibre.1791 - Heated factories
James Watt heats his factories through piped steam. He patents this method in the same year.1787 - Steamboat
American clock-maker John Fitch demonstrates the first steamboat.1779 - Spinning mule
Samuel Crompton invents the spinning mule (or cotton mule), allowing for greater control over the weaving process. It allows extremely fine yarn to be produced, allowing muslin to be made; previously this could only be made using hand-spun yarn from India.
1778 - Water closet
Joseph Bramah patents his water closet. The design was a success and production continued well into the 19th century. His original water closets are still working in Osbourne House, Queen Victoria's home on the Isle of Wight.1769 - Steam wagon
Nicolas-Joseph Cugnot demonstrates a 'steam wagon', predecessor to the first automobile.1769 - Spinning frame
Richard Arkwright invents a spinning frame (or water-frame) adapted to use water power. This made much cheaper manufacture possible, subsequently a great expansion of the cotton industry followed.1764 - Spinning Jenny
1757-1769 - Watt steam engine
James Watt patents his steam engine with separate condenser in 1769. Work begun in 1757. Also known as the Boulton & Watt steam engine.1755 - Sewing machine
The first recorded patent for a sewing machine is issued. It is a British patent issued to German Charles Weisenthal.1733 - Flying shuttle
John Kay invents the flying shuttle. This device makes mass production of textiles a possibility for the first time.1712 - Newcomen steam engine
Thomas Newcomen develops a working atmospheric steam engine, the first of its kind.1698 - Savery steam engine
1690 - Piston
Denis Papin uses steam to move a piston.1673 - Huygens motor
Christiaan Huygens builds a gunpowder explosion-driven motor.1629 - Branca steam turbine
1620-1624 - Submarine
Cornelius Drebbel invents the first submarine, a human-powered submersible. He holds successful trials in the Thames in 1624.1589 - Knitting machine
William Lee invents the knitting machine.1578 - Underwater rowing boat
Mathematician and innkeeper William Bourne designs an underwater rowing boat, covered in waterproof leather. The design is never built.1493 - Concept of flight
Leonardo da Vinci conceives of flying machines, creating over 100 sketches to illustrate his ideas.1440 - Printing press
The modern printing press is invented by Johannes Gensfleisch Gutenberg.1326 - Prototype handgun
1185 - Post windmill
The first recorded use of a post windmill, in Yorkshire. The first were of the sunken type.1150 - Tidal mills
Tidal mills are documented as being in use in England and France.1050 - Steel
Precursor to the modern Bessemer process that uses partial decarbonization via repeated forging under a cold blast is documented as being in use.
1010 - Human flight
First human flight, according to popular myth. Inspired by the Greek myth of Icarus, Brother Elmer (a monk at Malmesbury Abbey) creates a glider from wood and either linen or parchment. Launching himself from a height of around 18 metres, he flies 200 metres before panicking and crashing, breaking both of his legs.
650 - Windmill
The horizontal windmill is in use in Iran and Afghanistan.644 - Wind-power
A wind-power machine is developed by the Persians.62 - Æolipile
The æolipile, a simple steam engine, is invented by Hero of Alexandria.circa 3000 BC - Potter's Wheel
The potter's wheel is invented.circa 3300 BC - First sailing ship
The first depiction of a ship using cloth sails, in Egyptian paintings.circa 4000 BC - First wheeled vehicle
The first depiction of a wheeled-vehicle is on a pot from Southern Poland. It shows a wagon with four wheels and two axles.
circa 6000 BC - First boats
First depictions of canoes, dugouts and rafts in Egyptian rock paintings.





_-_filtered.jpg)





















































































































.jpg)









No comments:
Post a Comment